Special-purpose computer for holography: HORN
In electro-holography, a real-time reconstruction is one of grand challenges. To realize 3-D TV by electro-holography, we have developed special-purpose computing systems for CGH (computer-generated hologram), named HORN (Holographic Reconstruction), since 1992.
HORN-1 (1993) [1][2]
Tomoyoshi Ito designed and built the first special-purpose computer for holography, HORN-1 in March 1993. All chips (26 ICs) were mounted on a universal board by wire-rapping.

HORN-2 (1994) [3]
Tomoyoshi Ito designed and built HORN-2 in March 1994. In HORN-2, we used DSP (Digital Signal Processor) chips for high-accuracy computing (32-bit single precision). We made three boards and succeeded in operating three board in parallel.
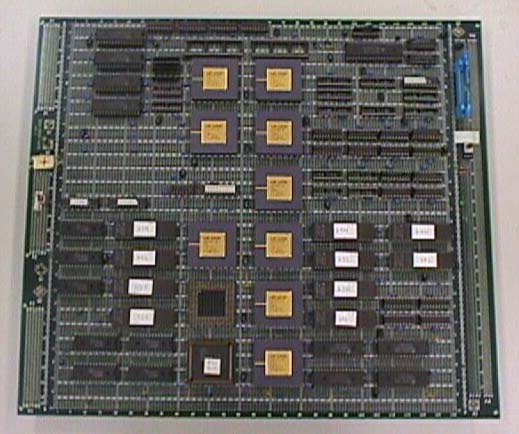
HORN-3 (1997) [4]
Tomoyoshi Shimobaba and Tomoyoshi Ito designed and built HORN-3 using PLD (Programmable Logic Device) technology in July 1997. We integrated a pipelined circuit to calculate hologram into one PLD chip (FLEX EPF10K70RC-2 by ALTERA), so that we could readily parallelize the system. In HORN-3, we mounted two PLD chips on a PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) universal board and succeeded in operating two CGH pipelines in parallel on one board.

HORN-4 (2001) [5][6]
Tomoyoshi Shimobaba and Tomoyoshi Ito designed and built HORN-4 using FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) technology in January 2001. For HORN-4, we developed an efficient algorithm of CGH calculation suitable for hardware devices, which could compute a phase on a hologram only by addition [6]. We designed and developed the pipelined circuit by the proposed algorithm and implemented the 21 pipelines into one FPGA chip (EP20K300EQC240-1 by ALTERA) We mounted two FPGA chips on HORN-4. In HORN-4, we succeeded in parallel calculations on a chip.
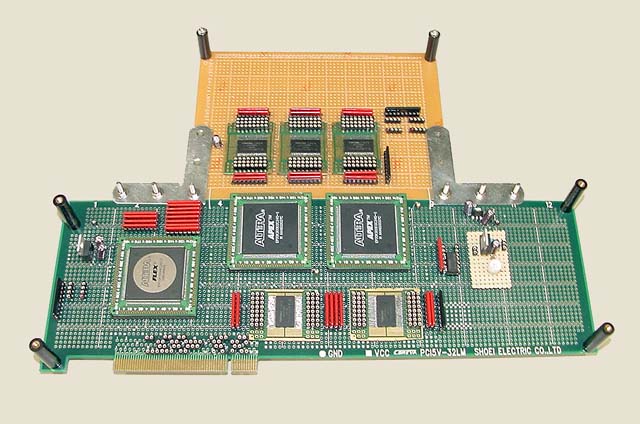
HORN with a display unit (2003) [6][7]
In the HORN project, one of goals is to build a HORN chip consisting both of a calculation circuit and a SLM (Spatial Light Modulator). Using HORN-4 architecture and a LCD (Liquid-Crystal Display), Tomoyoshi Ito and Tomoyoshi Shimobaba designed and developed the system by a board as the first challenge. We completed the manual assembly of the prototype system in February 2003. Then, we built the PCB (Printed Circuit Board). We hope to realize the system by one chip and to operate many chips in parallel. We think one of solutions to 3-D TV by electro-holography.
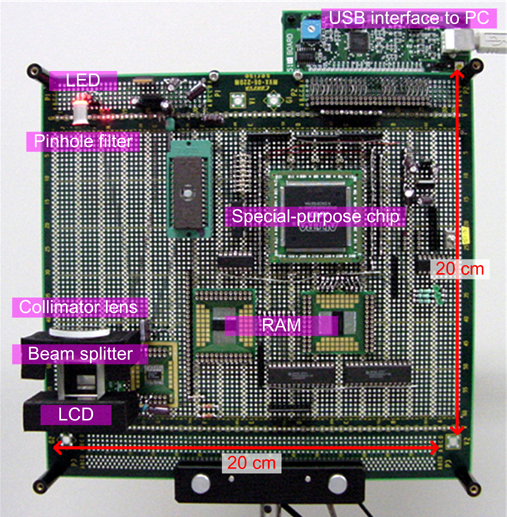
Hand-made proto type

PCB version
HORN-5 (2004) [8]
Tomoyoshi Ito, et. al., designed and built HORN-5 using large-scale FPGA technology in January 2004. On the board, four large-scale FPGA chips for CGH calculation, XC2VP70 by Xilinx, and one middle-scale FPGA chip for PCI control, XC2V1000 by Xilinx, were mounted. The number of the CGH pipelines was 352 per one FPGA chip and 1,408 per one board. We implemented four HORN-5 boards into one PC (Personal Computer). The performance of HORN-5 was 1,000 times higher than PC. We succeeded in video rate (30 fps: frames per second) for a 3-D object consisting of 10,000 points.
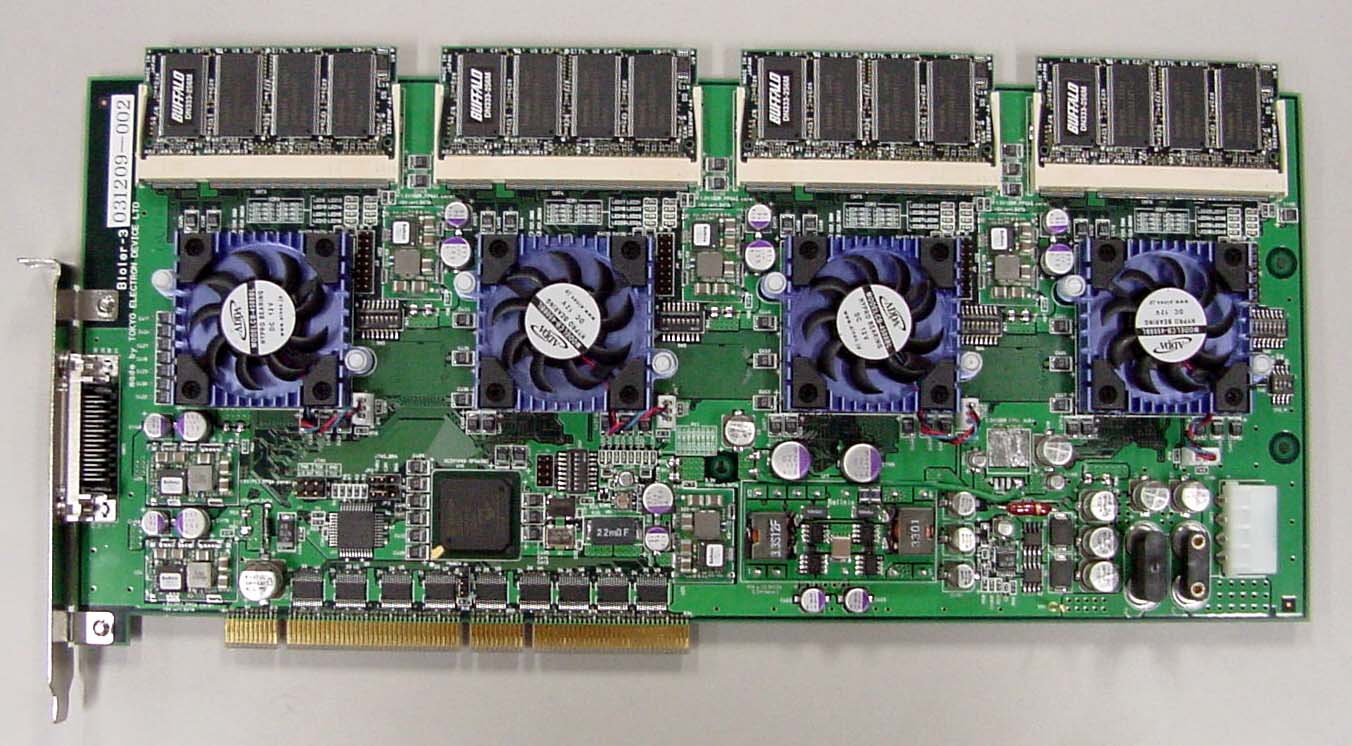
HORN-5 board
.jpg)
PC with four HORN-5 boards
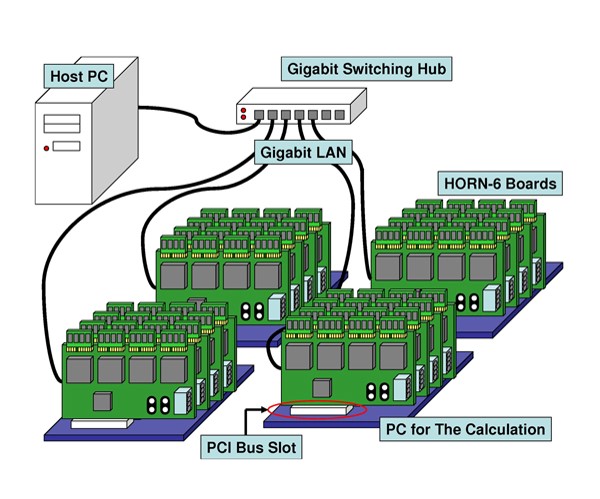
HORN-6 (2008) [9]
Yasuyuki Ichihashi, et. al., designed and built HORN-6 using highly parallel processing technology. We re-designed the circuit on the HORN-5 board and built PC cluster system with 16 HORN-5 boards. Total number of the CGH pipelines was 20,480. They operated simultaneously in parallel and the performance was 5,000 times higher than PC.
HORN-7 (2012) [10]
Nobuyuki Masuda, et. al., designed and built HORN-7 for phase modulation type hologram, using a commercial FPGA board, Vertex-6 ML605 by Xilinx. In image quality, phase modulation type hologram is superior to amplitude modulation type. Since a phase modulation type LCD was getting available commercially at that day, we adopted the phase modulated CGH to the HORN system.
HORN-8 (2015)
Takashige Sugie, et. al., designed and built HORN-8 using highly parallel processing technology with large-scale FPGA. Now, we do final tune-up. We report the details soon.
Short history video until 2009 (Sorry, in Japanese)
References
- Takashi Yabe, Tomoyoshi Ito and Masashi Okazaki, “Holography Machine HORN-1 for Computer-Aided Retrieval of Virtual Three-Dimensional Image”, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Vol.32, pp.L1359-L1361 (1993) [link]
- Tomoyoshi Ito, Takashi Yabe, Masashi Okazaki and Masanori Yanagi, “Special-Purpose Computer HORN-1 for Reconstruction of Virtual Image in Three Dimensions”, Computer Physics Communications, Vol.82, pp.104-110 (1994) [link]
- Tomoyoshi Ito, Hesham Eldeib, Kenji Yoshida, Shinya Takahashi, Takashi Yabe and Tomoaki Kunugi, “Special-Purpose Computer for Holography HORN-2”, Computer Physics Communications, Vol.93, pp.13-20 (1996) [link]
- Tomoyoshi Shimobaba, Nobuyuki Masuda, Takashige Sugie, Satoru Hosono, Shinobu Tsukui and Tomoyoshi Ito, “Special-purpose computer for holography HORN-3 with PLD technology”, Computer Physics Communications, Vol.130, pp.75-82 (2000) [link]
- Tomoyoshi Shimobaba and Tomoyoshi Ito, “An efficient computational method suitable for hardware of computer-generated hologram with phase computation by addition”, Computer Physics Communications, vol.138, pp.44-52 (2001) [link]
- Tomoyoshi Shimobaba, Sinsuke Hishinuma and Tomoyoshi Ito, “Special-Purpose Computer for Holography HORN-4 with recurrence algorithm”, Computer Physics Communications, Vol.148, pp.160-170 (2002) [link]
- Tomoyoshi Ito and Tomoyoshi Shimobaba, “One-unit system for electroholography by use of a special-purpose computational chip with a high-resolution liquid-crystal display toward a three-dimensional television”, Optics Express, Vol.12, No.9, pp.1788-1793 (2004) [link]
- Yasuyuki Ichihashi, Nobuyuki Masuda, Munenori Tsuge, Hirotaka Nakayama, Atsushi Shiraki, Tomoyoshi Shimobaba and Tomoyoshi Ito, “One-unit system to reconstruct a 3-D movie at a video-rate via electroholography”, Optics Express, Vol.17, Issue 22, pp.19691-19697 (2009.10) [link]
- Tomoyoshi Ito, Nobuyuki Masuda, Kotaro Yoshimura, Atsushi Shiraki, Tomoyoshi Shimobaba and Takashige Sugie, “A special-purpose computer HORN-5 for a real-time electroholography”, Optics Express, Vol.13, No.6, pp.1923-1932 (2005) [link]
- Yasuyuki Ichihashi, Hirotaka Nakayama, Tomoyoshi Ito, Nobuyuki Masuda, Tomoyoshi Shimobaba, Atsushi Shiraki and Takashige Sugie, “HORN-6 special-purpose clustered computing system for electroholography”, Optics Express, Vol.17, Issue 16, pp.13895-13903 (2009) [link]
- Naohisa Okada, Daichi Hirai, Yasuyuki Ichihashi, Atsushi Shiraki, Takashi Kakue, Tomoyoshi Shimababa, Nobuyuki Masuda and Tomoyoshi Ito, "Special-Purpose Computer HORN-7 with FPGA Technology for Phase Modulation Type Electro-Holography", 19th International Display Workshops in conjunction with Asia Display 2012 (IDW/AD' 12), 3Dp-26, Kyoto International Conference Center, Kyoto, Japan (2012.12.4-7)